INDIA UNION BUDGET 2025 -26
-

The budgetary support for on grid solar energy under union budget 2025-26 is INR 1500 crores. This is 85% less than that announced in the budget of 2024-25.
Revised allocation for 2024-25 is significantly low which may be indicative of delay in realization of projects. -

The allocations for PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana and PM Kusum Scheme has seen increase from 2024-25 due to positive response for these scheme shown by the country.
PM SGMBY has helped increase the adoption of solar rooftop across the country.
-
-
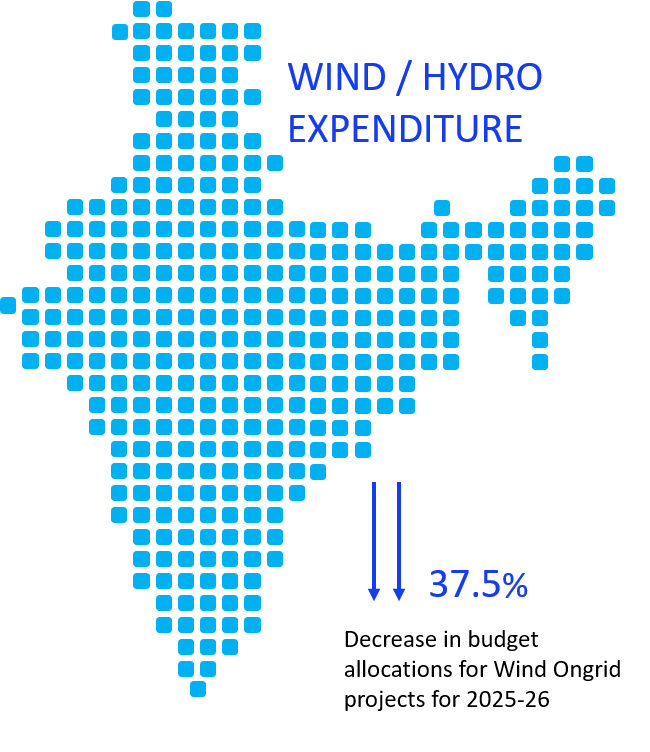
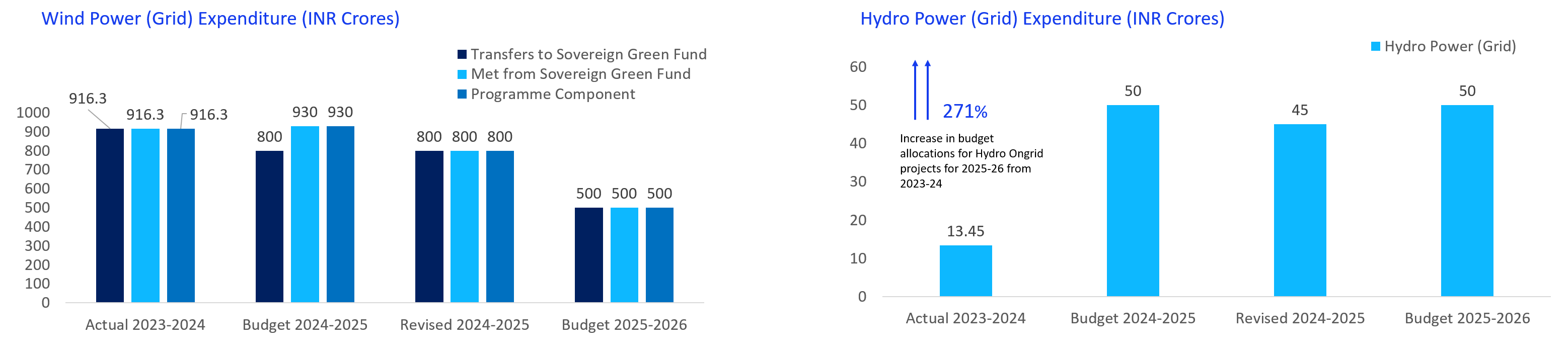
The budgetary support for wind energy under union budget 2025-26 is INR 500 crores. This is 37.5% less than that announced in the budget of 2024-25. GoI is giving impetus on increasing standalone onshore and offshore wind projects as well as hybrid projects. Does this decline in the support indicates a shift in the focus of government? The budgetary support for hydro energy under union budget 2025-26 is INR 50 crores.
The allotment of funds to hydro energy have seen significant rise of 271% from 2023-24 to union budget of 2024-25 and 2025-26. This increase may be due to increase focus on developing pumped hydro storage projects in the country for supporting round the clock power supply.
-
-

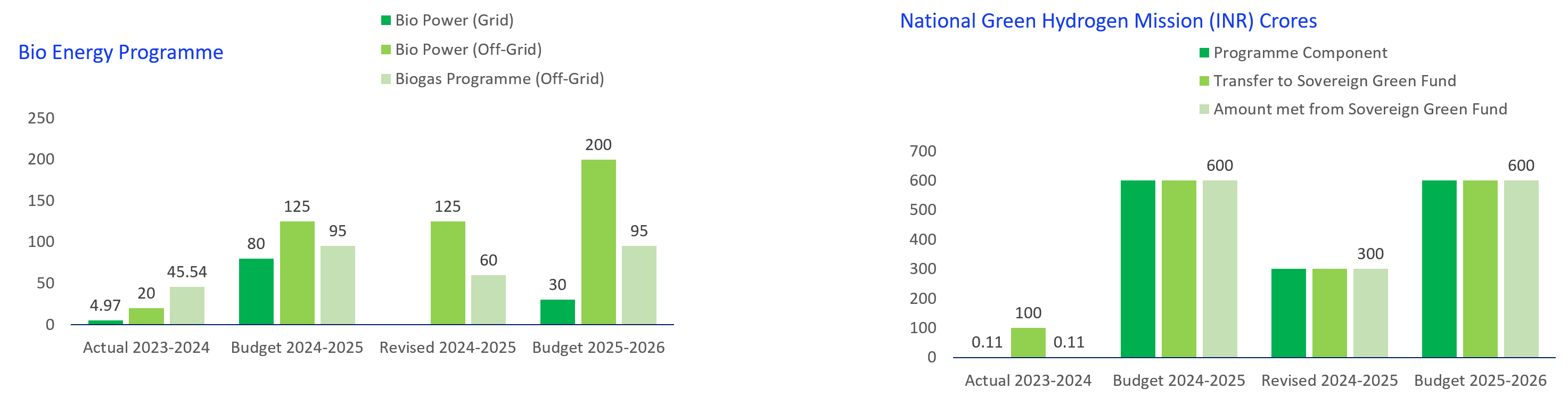
The budgetary support for grid connected bio power under union budget 2025-26 is INR 30 crores.
This is 62.5% less than that announced in the budget of 2024-25 while for off grid bio power the expenditure has seen an increase of 60% to 200 crores from that of 124 crores in budget of 2024-25. -
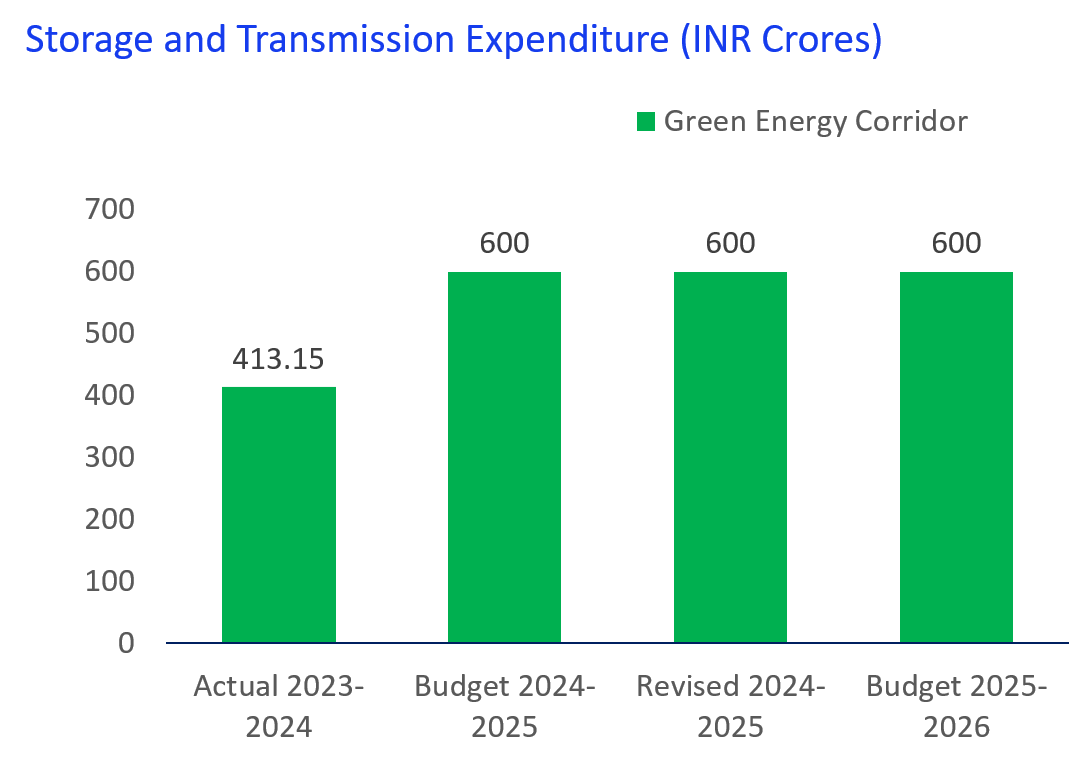
The fund support for storage and transmission system and national green hydrogen mission has been consistent from FY 2024-25 to FY 2025-26 representing GoI’s efforts to diversify India’s energy mix promoting innovation in the sector of energy storage and making India world leader in the production and export of green hydrogen.
-
The increase in budgetary support for IREDA to ₹34,974.99 crore in FY 2025-26 signals a stronger commitment by the government to accelerate the growth of renewable energy in India. This boost reflects a focus on expanding renewable energy capacity, meeting climate targets, and enhancing financial support for clean energy projects.
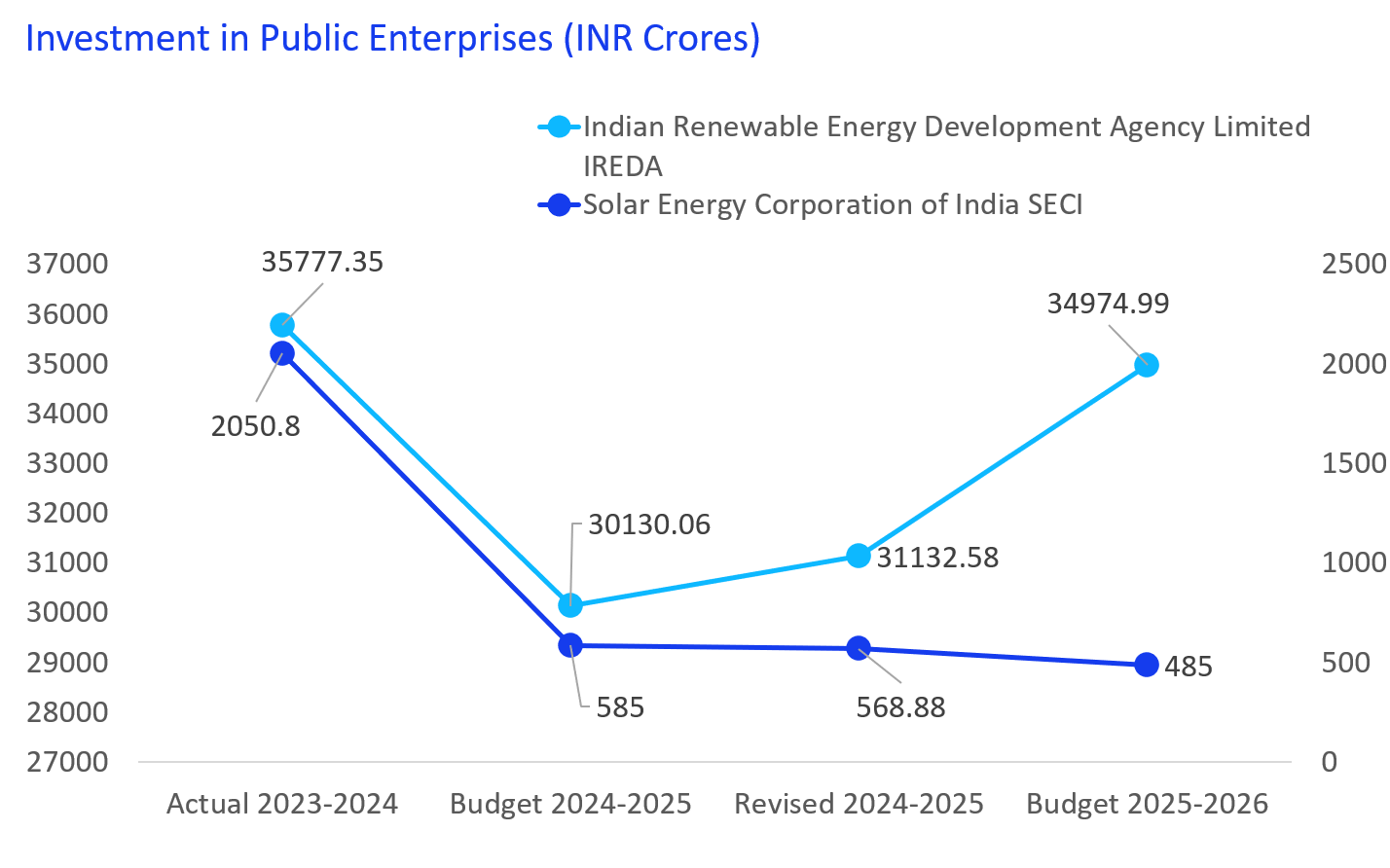
The funds are likely to strengthen IREDA’s role in financing innovation, and energy storage solutions, thus contributing to India’s transition towards a sustainable energy future. While decrease in the allocations for SECI may represent the trend of delay in progress of bids and realization and commission of the renewable projects which may be due to supply chain or land availability issues.
-
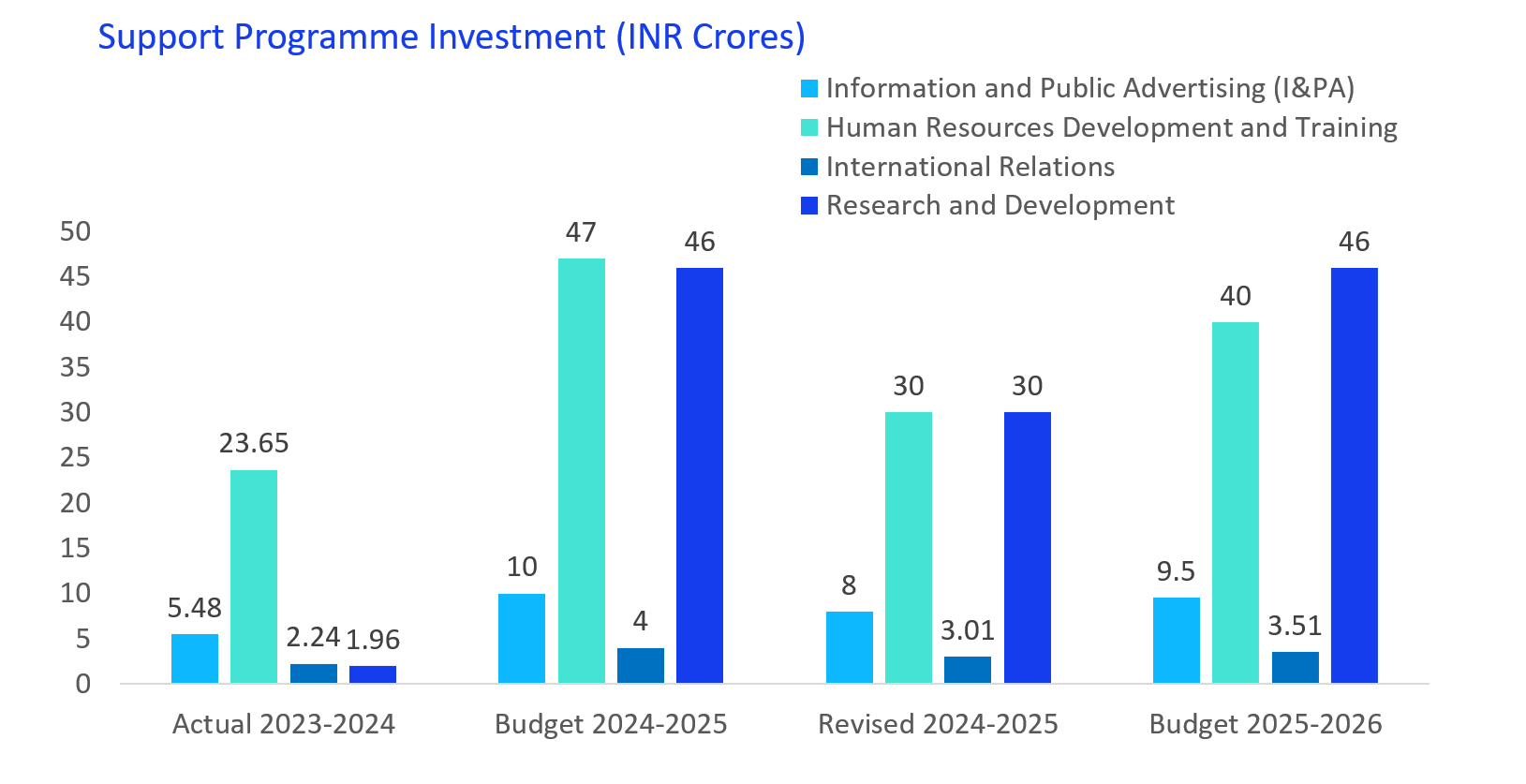
The increase in central spending on programs like Information and Public Advertising (I&PA), Human Resources Development and Training (HRDT), International Relations, and Research and Development (R&D), with a significant importance for R&D and HRDT, indicates a strong focus on strengthening the country’s knowledge economy, global presence, and human capital.
The expenditure in R&D suggests a push for innovation and technological advancements, while allocation for HRDT reflects an emphasis on skill development, workforce training, and capacity building. Together, these efforts highlight the government’s intent to foster growth through enhanced research, global collaboration, and a more skilled workforce to drive national progress.




