Will India's hydrogen production cost competitiveness unlock global market opportunities or remain limited by infrastructure and feedstock constraints?
- What are key materials for hydrogen storage and transport?
- Which global best practices can India adopt and localize?
- How can India capture a $25B hydrogen materials opportunity?
- How big is the global and Indian market opportunity for H2 storage material by 2040?
Strategic assessment of the $200B global market in hydrogen storage materials, with India’s $25B opportunity in technology, policy, and manufacturing.
-
Why is a comprehensive assessment of hydrogen production cost competitiveness critical to unlocking India’s global market potential—spanning green hydrogen exports, industrial decarbonization, and domestic mobility, while informing strategic decisions for public sector undertakings, private developers, electrolyzer OEMs, and infrastructure planners?
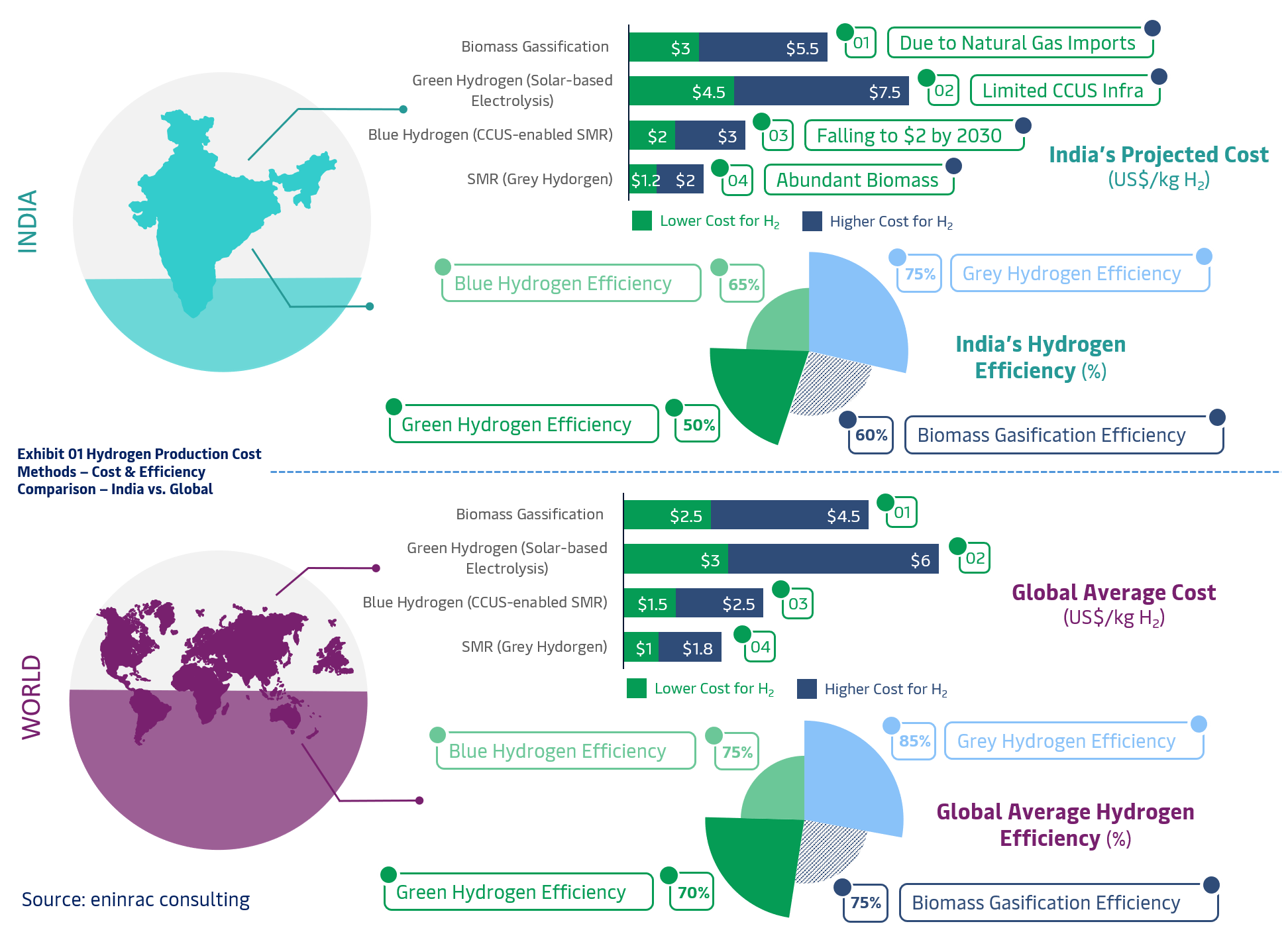
Hydrogen production costs and efficiencies vary
widely by method and geography. In India, reliance on imported
natural gas raises the cost of grey and blue hydrogen compared to
global averages. While green hydrogen remains costlier today,
aggressive renewables expansion and policy support are
expected to bring costs down to ~$2/kg by 2030.
Biomass gasification, leveraging India’s agricultural residue,
offers a promising decentralized route. This comparative analysis
highlights how India’s hydrogen strategy must balance technology
maturity,
For in-depth data, technology readiness levels, and cost forecasts
across hydrogen production pathways
download our exclusive market report here.
feedstock availability, and infrastructure readiness to realize
its green hydrogen ambitions.
Further, aligning cost competitiveness with global benchmarks is essential for India to emerge as a key hydrogen exporter. Electrolyzer localization, viability gap funding, and scale-driven cost reductions will be crucial. Strategic production clusters near RE zones, ports, and industrial hubs can enhance economics. Policy clarity and cross-sectoral coordination will determine India’s pace in capturing its share of the $100B+ global green hydrogen trade opportunity. Moreover, regional production incentives, carbon pricing mechanisms, and renewable energy banking policies will shape investor confidence. India's ability to integrate hydrogen into refining, fertilizer, steel, and mobility sectors will directly influence demand scaling. The convergence of public-private capital, innovation ecosystems, and strategic international partnerships will define India’s leadership in the hydrogen economy.
How Are Global and Indian Hydrogen Storage Trends Shaping Up? Insights by Eninrac Analysts
-
Understanding hydrogen storage trends is key to building a robust hydrogen economy. Eninrac analysts assess emerging technologies—like compressed gas, cryogenic liquid, hydrides, and LOHCs—highlighting their market potential, efficiency, and material challenges. With India targeting leadership in green hydrogen, decoding storage economics and readiness becomes vital for OEMs, policymakers, and investors eyeing a share in the $30B+ global opportunity.
Hydrogen storage remains a critical enabler for realizing the hydrogen economy—impacting transport, distribution, and end-use efficiency. As per Eninrac’s market intelligence, the global hydrogen storage market is poised to cross $30 billion by 2030, with India contributing an estimated $2.4 billion, led by compressed gas and emerging cryogenic solutions.
Compressed hydrogen gas storage (350–700 bar) continues to dominate early deployments, but its low energy density (1.2–1.5 kWh/kg) and energy-intensive compression present safety and cost trade-offs. India’s share in this segment is projected at $1.2 billion, driven by mobility and backup power applications. However, advanced Type IV tank materials and improved valve technologies remain critical to cost optimization. In parallel, liquid hydrogen (LH2) offers higher energy density (2.3–2.8 kWh/kg), yet faces challenges of ~1% daily boil-off losses, impacting viability in long-haul and maritime use cases. Eninrac analysts note India’s LH2 potential at $0.5 billion, backed by ISRO’s legacy and recent public-private interest. Metal hydrides (e.g., MgH₂) and Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHCs) are gaining traction in R&D and pilot phases. While their energy densities range from 1.5 to 2.2 kWh/kg, their limitations—such as slow kinetics for hydrides and high regeneration temperatures for LOHCs—require further breakthroughs.
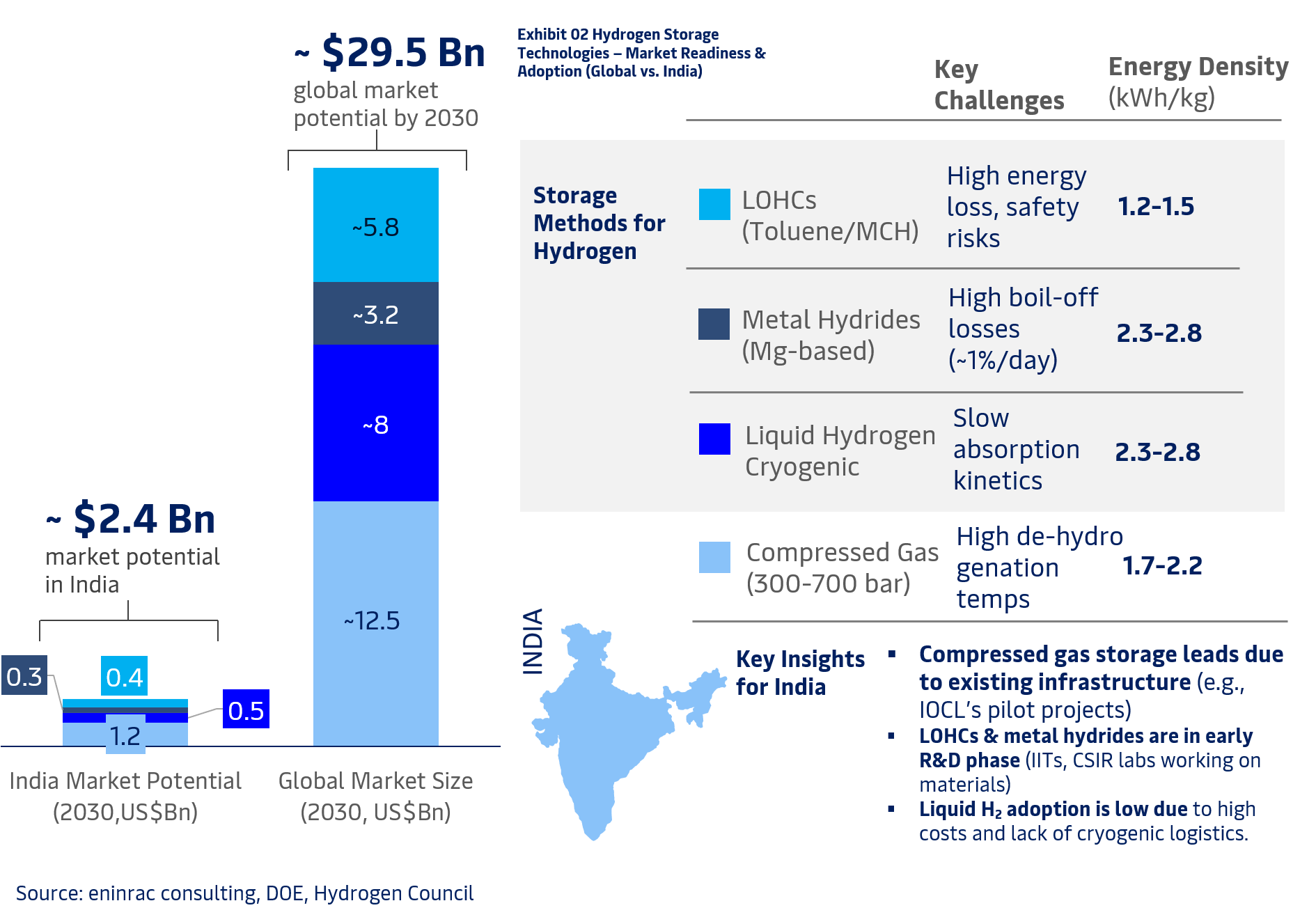
Team Eninrac’s assessment underscores that a diversified storage portfolio, tailored by application (stationary, mobility, maritime) and aligned with material science innovations, will be vital to India’s competitive positioning in the $200B+ global hydrogen value chain.
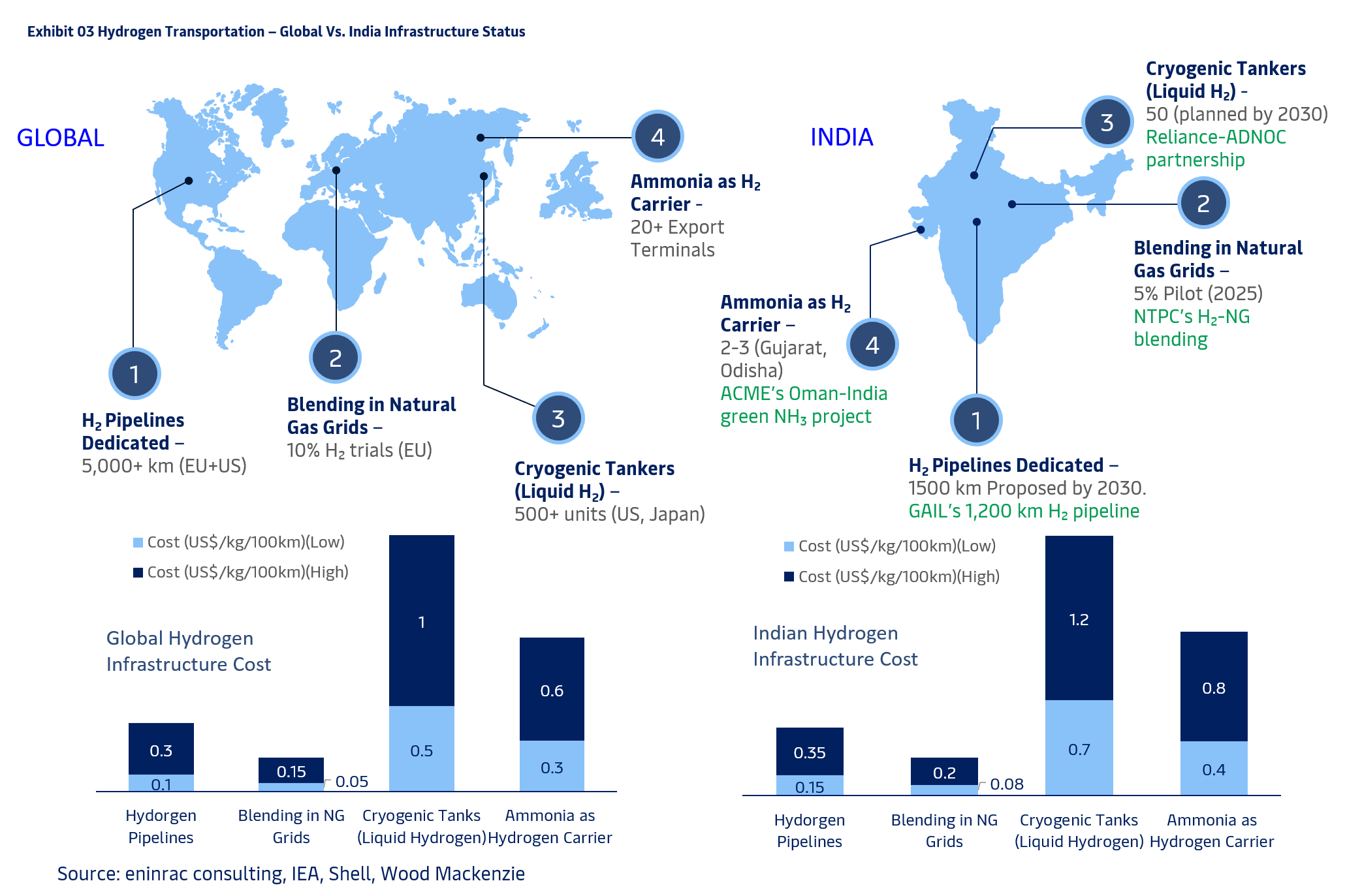
How Does India’s Hydrogen Transportation Infrastructure Compare with Global Benchmarks?
India’s hydrogen transportation infrastructure is gradually aligning with global benchmarks. Eninrac’s market research reveals that while the EU and U.S. lead with 5,000+ km of dedicated hydrogen pipelines, India is targeting 1,500 km by 2030 led by GAIL’s 1,200 km project. Blending hydrogen into natural gas grids is also gaining traction, with NTPC spearheading 5% pilot programs. On the cryogenic front, India plans 50+ liquid hydrogen tankers, compared to 500+ globally. Meanwhile, green ammonia is emerging as a viable export carrier, with terminals in Gujarat and Odisha planned by 2030. As India builds out this logistics backbone, infrastructure investments will be pivotal in unlocking cost-efficient hydrogen delivery.
Eninrac analysts highlight that transport mode selection must
balance cost, scalability, and technological maturity. While pipelines offer long-term economic advantages for bulk
transport, blending remains a quick-start solution for early market
activation. Cryogenic and ammonia-based routes will likely dominate
export-oriented strategies, especially with Reliance, ACME, and
Greenko actively pursuing partnerships. The development of
standards, right-of-way frameworks, and carrier-specific safety
protocols will be vital.
India’s success in this space will hinge on synchronized action
between public utilities, private developers, and regulatory bodies
under the National Green Hydrogen Mission. Furthermore, leveraging
India's existing gas infrastructure for low-blend hydrogen
integration could reduce near-term CAPEX and fast-track regional
hydrogen hubs. Eninrac analysts also emphasize the importance of
indigenizing tanker manufacturing and developing specialized port
infrastructure to handle ammonia and liquid hydrogen safely. As
global hydrogen trade corridors evolve, India’s proactive alignment
with international codes and certification standards will be crucial
for market access and competitiveness.