TBCB GUIDELINES FOR PROCUREMENT OF STORAGE CAPACITY – INDIA
Analysis of Ministry of Power Resolution of TBCB Guidelines for Procurement Storage Capacity & Stored Energy from PHSP
DESCRIPTION OF THE RESOLUTION
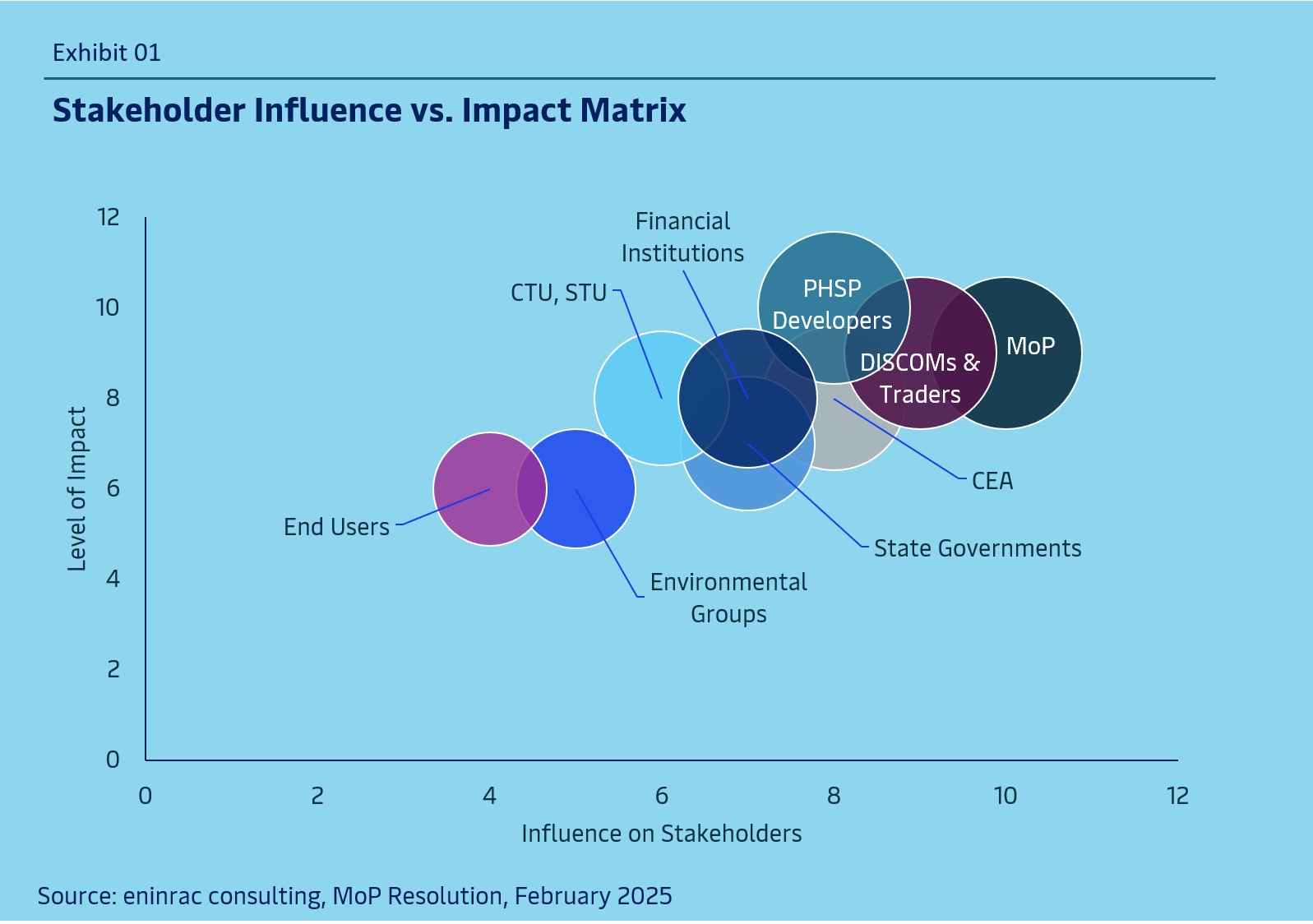
Tariff-Based Competitive Bidding Guidelines for the procurement of storage capacity or stored energy from Pumped Storage Plants (PSPs), issued by the Ministry of Power (MoP), India aims to support India's energy transition by enhancing grid stability, integrating renewable energy sources, and reducing peak-time electricity costs. The guidelines establish a transparent, standardized framework for procurement, ensuring fair risk-sharing among stakeholders, including developers, procurers, financial institutions, and regulatory bodies.
Key provisions include bidding structures, financial eligibility criteria, performance guarantees, and contract terms. The document also outlines the technical requirements, project timelines, and tariff structures for PSP development. Additionally, it highlights environmental considerations, land acquisition policies, and social impact assessments. By defining clear regulatory processes and dispute resolution mechanisms, these guidelines aim to attract investment, improve energy security, and drive long-term sustainability in India's evolving power sector.
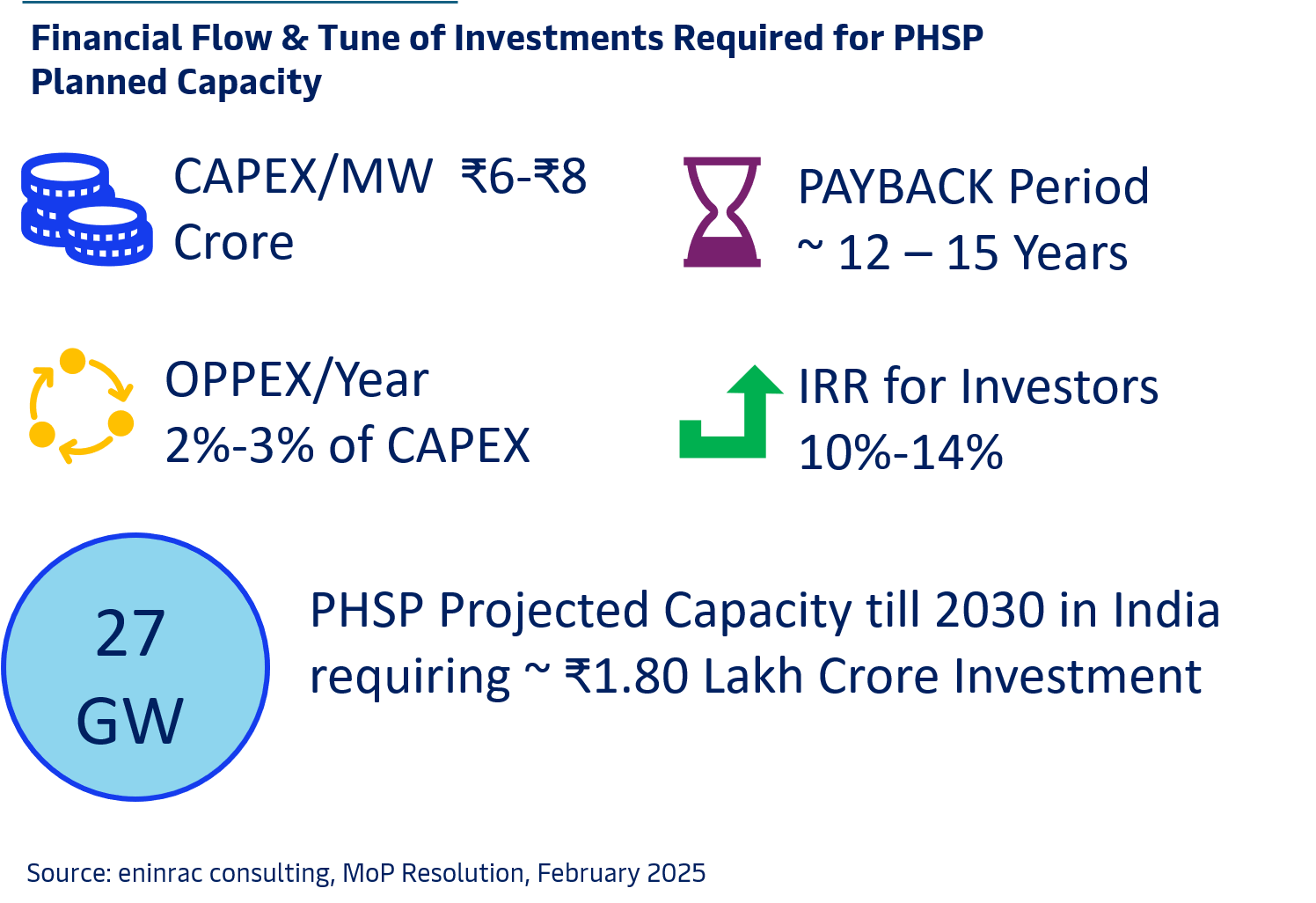
The policy supports the National Electricity Plan 2023, which projects a need for 27 GW of PSP capacity by 2031-32. It enables cost-effective peak load management, reduces carbon emissions, and encourages public-private partnerships (PPPs) to accelerate storage infrastructure development while balancing economic and environmental factors.
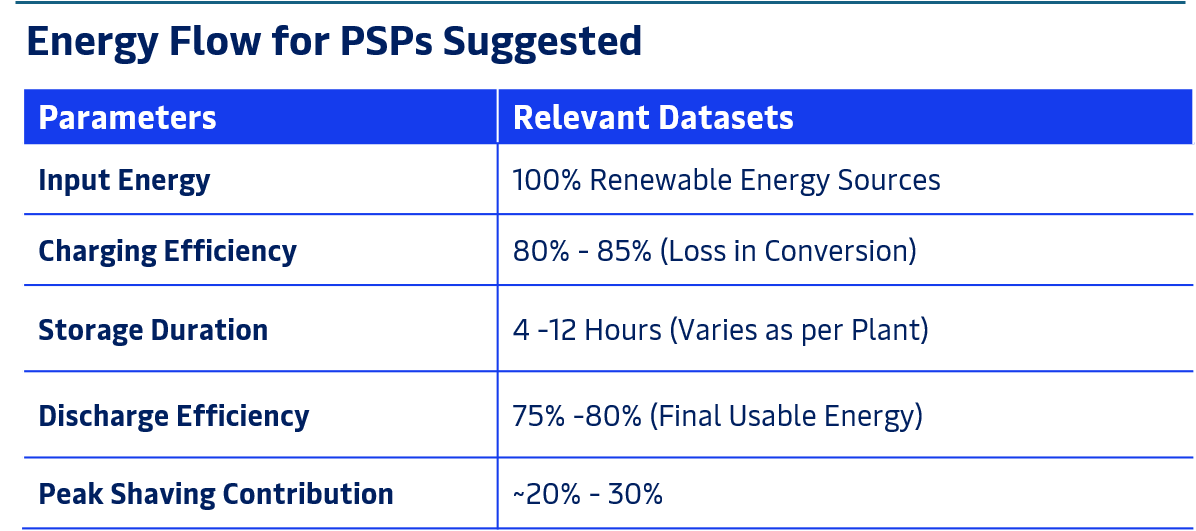
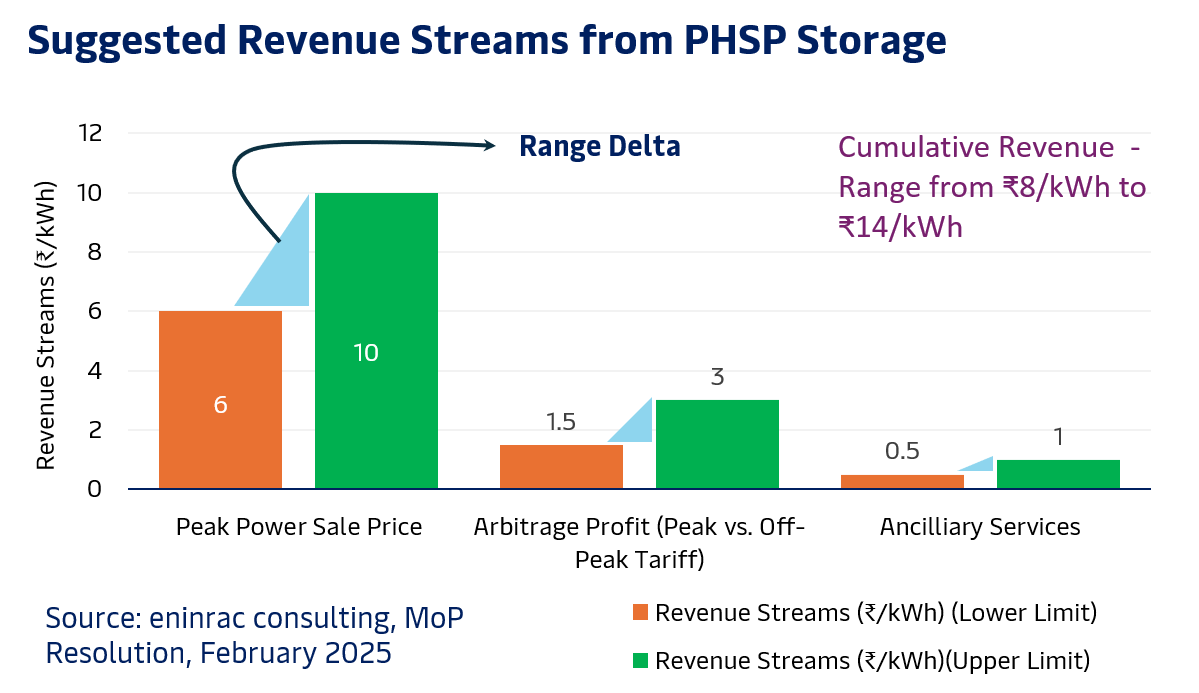
ENERGY FLOW & ECONOMIC BENEFITS OF PHSPs
FINANCIAL FLOW & INVESTMENT REQUIREMENT - PHSP
The policy supports the National Electricity Plan 2023, which projects a need for 27 GW of PSP capacity by 2031-32. It enables cost-effective peak load management, reduces carbon emissions, and encourages public-private partnerships (PPPs) to accelerate storage infrastructure development.
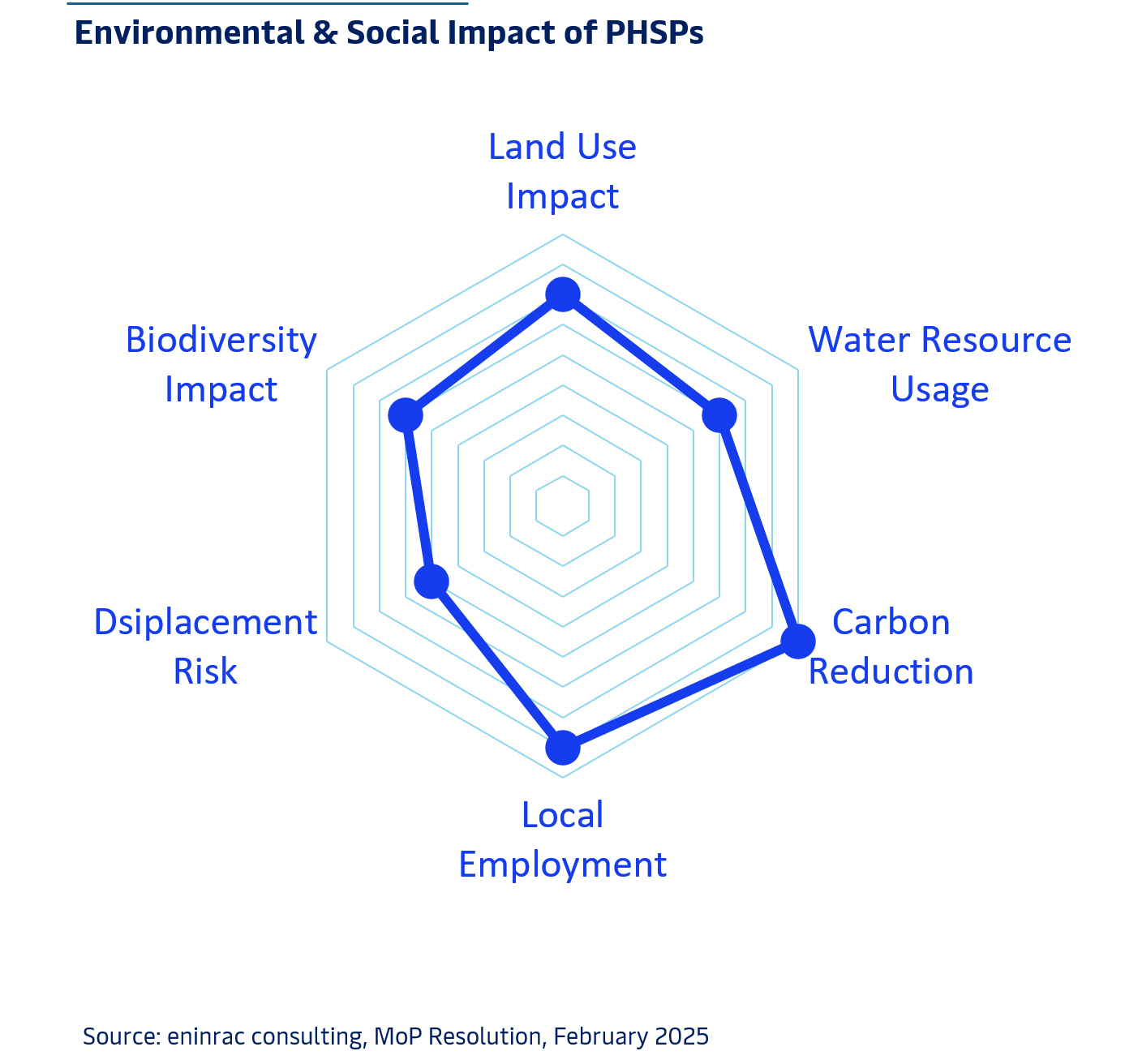
ENVIRONMENT & SOCIAL IMPACT
KEY IMPACTS
Pumped Storage Plants (PSPs) play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions by integrating renewable energy and minimizing reliance on fossil-fuel-based power generation. However, their development comes with environmental and social considerations.
PSPs require large reservoirs, which can lead to land acquisition challenges, deforestation, and ecosystem disturbances. Water resource management is a key concern, as PSPs may alter river flows and affect aquatic biodiversity. Additionally, local communities near project sites may face displacement and livelihood disruptions, necessitating resettlement plans and fair compensation.
To mitigate these impacts, PSP projects must undergo environmental impact assessments (EIA), adhere to sustainability guidelines, and implement afforestation programs. Proper stakeholder engagement and community development initiatives are essential to balancing economic benefits with ecological and social responsibility.




